Alignment (IE/IEX only)
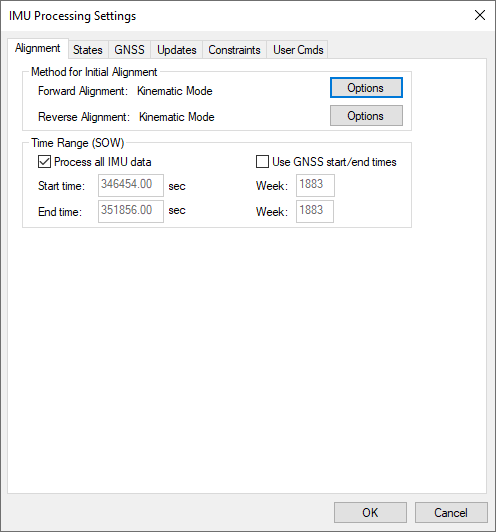
Method for Initial Alignment
In INS processing, small changes in velocity and orientation are integrated in order to derive position, velocity and attitude from a starting point. As such, it is a relative positioning method and the initial integration conditions must be known. Alignment is the process of solving these initial integration constants.
The initial position and velocity of the IMU are usually derived from Inertial Explorer's GNSS processor. Initial roll and pitch are derived from the accelerometer measurements and initial heading is derived from gyroscope measurements.
IMUs of tactical grade or higher are capable of static alignment. However MEMS IMUs, or any IMU with a gyro bias larger than the Earth rate (15 deg/hr at the equator), are not capable of deriving a reliable heading from gyro measurements alone. In these cases, the GPS Course-Over-Ground (COG) must be used to help Inertial Explorer determine the initial azimuth of the IMU.
Click the Options button to open the Align Options dialog. See Align Options for information about the settings available on this dialog.
Time Range Options
Process All IMU Data
If this option is enabled, the software obtains the beginning and end times from the raw binary IMU file. These times are in GPS seconds of the week.
Use GNSS start/end times
When selected, IMU processing will start and end based on a time range set under the General tab of the GNSS processing options menu.
Start Time
Forward alignment will begin at the entered time (GPS SOW). Reverse processing will end at this time.
End Time
Reverse alignment will begin at the entered time (GPS SOW). Forward processing will end at this time.