SPAN Data Logging for Inertial Explorer
This document provides an overview of the OEM7 SPAN logs used for post-processing in Inertial Explorer. A list of required logs outlines the minimum logging requirements needed for post-processing. Additional logs are recommended for increased ease of use, specific applications, and troubleshooting purposes. Example lists of commands and logs are provided at the end of the document, which can be used as templates for basic data collections.
Data logging
Log types and headers
There are multiple logging formats which can be used to record NovAtel receiver data. Table: Logging different formatting types provides a summary of these formats and select examples. It is recommended to log data records in binary format, as the NovAtel/OEM decoder in Inertial Explorer supports only binary logs. After data conversion, all decoded logs will be displayed in the conversion summary. Further details on data types and log formats can be found in the OEM User Manuals.
Logging triggers & frequency
The choice of logging triggers depends on the log itself and how the data is used in post-processing. Each log trigger outputs the current message immediately after it has been called. Below is a summary of the available logging triggers:
|
ONCE: |
Outputs the current message only once. |
|
ONCHANGED: |
Outputs the current message and then continues to output only when the values in the message are changed. |
|
ONNEW: |
Does not output the current message but outputs every time the message is updated. |
|
ONTIME <#>: |
Outputs the message at regular intervals of <#> seconds during data collection. |
|
ONALL: |
Outputs the current message and then continues to output whenever the message is updated or changed. |
The ONCHANGED trigger offers benefits such as avoiding duplicate logs and minimising file size. However, if an ONCHANGED log request is made before the logging file is opened, the log will not be triggered until a value changes. This can be problematic during short surveys, as logs with slow-changing values (e.g., RAWEPHEMB) may not be recorded within the data collection period.
To address this limitation, the ONNEW trigger has been recommended for short surveys when using firmware versions earlier than 7.09.01. However, ONNEW does not output the current message, potentially creating a gap in the data.
To resolve this, the ONALL trigger was introduced in firmware version 7.09.01 and later. ONALL ensures optimal data coverage by outputting the current message and continuing to output whenever the message is updated or changed. ONALL is now the preferred trigger option for most use cases moving forward.
When using the ONCE trigger, the user must ensure that the logging file has been opened before the log call. If not, the information will not be saved anywhere in the file, as the log will not be called again. During INS operation, the highest rate at which GNSS logs should be requested is 5 Hz (0.2 seconds). For the RANGE log, the recommended rate is 2 Hz for GNSS and INS integration. Common GNSS logs include, but are not limited to RANGE, BESTPOSB, BESTGNSSPOSB, RTKPOSB and PSRPOSB.
SPAN logs
The following list outlines the logs required and recommended for post processing in Inertial Explorer. For differential processing, a subset of these logs must be logged at the base. The Required for note describes how Inertial Explorer uses the data provided in the log. Suitable Alternative logs are also listed, which can be selected based on user preference. The Used for note describes how Inertial Explorer uses the data provided in the log. Not all logs will be used in Inertial Explorer post-processing, however they can be Helpful for troubleshooting purposes and record keeping. Finally, Requirement notes outline prerequisite steps needed for the successful output of the log.
Required Logs
These logs are required to collect the raw data necessary for post-processing.
|
Log |
Receiver type |
Details |
|---|---|---|
|
LOG RANGEB ONTIME 0.5 |
Rover/Master |
Satellite range information. Channel measurements for the currently tracked satellites. Required for: GPB file creation and GNSS data processing; source of GNSS raw data. Alternatives: RANGECMPB, RANGECMP2B, RANGECMP4B |
|
LOG GPSEPHEMB ONALL |
Rover/Master |
GPS raw ephemeris information. Required for: Computing GPS satellite coordinates and elevation. Alternative: RAWEPHEMB |
|
LOG GLOEPHEMERISB ONALL |
Rover/Master |
GLONASS raw ephemeris information. Required for: Computing GLONASS satellite coordinates and elevation. Alternative: GLORAWEPHEMERISB |
|
LOG GALINAVEPHEMERISB ONALL |
Rover/Master |
Galileo INAV ephemeris information Alternative: GALEPHEMERISB |
|
LOG GALFNAVEPHEMERISB ONALL |
Rover/Master |
Galileo FNAV ephemeris information Alternative: GALEPHEMERISB |
|
LOG BDSEPHEMERISB ONALL |
Rover/Master |
BeiDou ephemeris information |
|
LOG QZSSEPHEMERISB ONALL |
Rover/Master |
QZSS ephemeris parameters |
|
LOG NAVICEPHEMERISB ONALL |
Rover/Master |
NavIC ephemeris information. |
|
LOG RAWIMUSXB ONNEW |
Rover only |
Raw gyroscope and accelerometer measurements, including an IMU status indicator. Required for: IMR file creation and INS data processing; provides sequential changes in velocity and rotation. Directions: Must log ONNEW. Use the extended header to include the name of the IMU. This helps to ensure correct conversion in Waypoint products. Alternatives: RAWIMUB, RAWIMUSB, RAWIMUXB |
Recommended logs
The following logs are not required for post-processing, but provide information that aids in project setup, data analysis, and troubleshooting. A number of logs specified below are used for extracting real-time trajectories to a Waypoint readable format. Instructions on how to generate these files are provided in Appendix A: Full project example.
|
Log |
Receiver type |
Details |
|---|---|---|
|
LOG VERSIONB ONCE |
Rover/Master |
Version information for all system components. Used for: Keeping record of the system components of the data collection. |
|
LOG RXCONFIGB ONCE |
Rover/Master |
Receiver configuration. List of all current command settings. Helpful for: Support and troubleshooting. Note: Log after the configuration commands are sent. |
|
LOG RXSTATUSB ONCE |
Rover/Master |
Receiver Status. List of GNSS receiver system status (health) parameters. |
|
LOG THISANTENNATYPEB ONCE |
Rover only |
Antenna model used by remote receiver Corrects vertical offset between where GNSS observations are observed (the electronic phase center) and the Antenna Reference Point (ARP) Corrects for any difference between the L1 and L2 electronic phase centers, which can be a factor in the success or failure of ambiguity resolution. Applies elevation-based corrections to the GNSS signal Helpful for: Auto filling remote antenna information during project creation Requirement: User must first set antenna prior to logging it (e.g., THISANTENNATYPE NOV850) |
|
LOG INSPVAXB ONTIME 1 |
Rover only |
INS position, velocity and attitude in the SPAN computation frame and their estimated errors. Used for: Extracting real-time trajectory to a Waypoint-readable format. Note: If high-rate INSPVA logs are needed, but bandwidth is a concern, use INSPVASB and INSSTDEVSB as alternatives. |
|
LOG BESTPOSB ONTIME 1 |
Rover only |
Best available combined GNSS and INS solution output at the GNSS phase center. Used for: Extracting real-time trajectory to a Waypoint readable format, and decoding position estimated by the receiver to the GPB file. |
|
LOG BESTGNSSPOSB ONTIME 1 |
Rover only |
Best available GNSS solution computed without INS. Used for: Extracting real-time trajectory to a Waypoint readable format. |
|
LOG TIMEB ONTIME 1 |
Rover/Master |
Time related information such as receiver clock offset, and UTC time and offset. Used for: Decoding receiver clock shift to GPB file. |
|
LOG INSCONFIGB ONCHANGED |
Rover only |
All IMU configuration parameters required for post-processing or system analysis. Used for: IMU alignment settings. Requirement: User must first set values using variations of the SETINSTRANSLATION and SETINSROTATION commands. |
For the commands specific to your system setup, see SPAN documentation.
Supplementary Logs: Common Applications
This section outlines the logs required for the integration of application-specific data in Inertial Explorer. Please note that this list contains only the logs required in Inertial Explorer and does not encompass all logs and commands required for the proper set up and real time tracking of these systems. Further information on application-specific setup can be found in the OEM User Manuals.
Dual antenna (ALIGN solution)
|
Log |
Receiver type |
Details |
|---|---|---|
|
LOG HEADING2B ONNEW |
Rover only |
Angle from true north of the base ALIGN antenna to the rover ALIGN antenna (positive clockwise direction). Used for: HMR file creation. Requirement: User must first set the two lever arm values using SETINSTRANSLATION ANT1, SETINSTRANSLATION ANT2. |
|
LOG RANGEB_1 ONTIME 0.5 |
Rover only |
Satellite range information for the secondary GNSS antenna. Required for: GPB file creation for the secondary antenna. This is not required in the default workflow, but can be useful for troubleshooting and computing the moving baseline vector in GrafNav software. Alternative: RANGECMPB_1 |
Wheel sensor (Distance Measurement Instrument – DMI)
|
Logs |
Receiver type |
Details |
|---|---|---|
|
LOG RAWDMIB ONNEW |
Rover only |
Time stamped raw wheel sensor data. Used for: Measurements in the DMR file Note: Available on firmware versions 7.07.00 and newer. |
|
LOG DMICONFIGB ONCHANGED |
Rover only |
Wheel sensor configuration. Used for: Setting the ID, availability and input type of DMI sensor(s). Requirement: User must first set these parameters before logging data from wheel sensor(s). Note: Available on firmware versions 7.07.00 and newer. Note: A maximum of 3 DMIs can be decoded to the DMR file, but Inertial Explorer will only process data from the first wheel sensor that is logging cumulative ticks. |
No RAWDMIB logs will be decoded without the presence of a DMICONFIGB log. As such, users may consider logging this ONTIME at a coarse rate to ensure it is saved to file (e.g. LOG DMICONFIGB ONTIME 300).
Miscellaneous
|
Log |
Receiver type |
Details |
|---|---|---|
|
LOG MARKTIMEB ONNEW |
Rover only |
Time of mark input event. Used for: Measure the time when events are occurring in other devices. Note: Other mark input event logs include MARK2TIMEB, MARK3TIMEB, and MARK4TIMEB. |
Appendix A: Full project example
This section provides an example of how a well-planned list of logs and commands will allow for an efficient workflow in Inertial Explorer. The following SPAN data collection uses GPS and GLONASS constellations, a dual antenna system, and is set up with the default IMU orientation (standard Y forward, Z up, X right). The equivalent OEM7 logs and commands used in this data collection are listed below to provide a summary example. The figures on the following pages demonstrate how the information from these logs is used in Inertial Explorer to convert and generate files and auto-fill set up parameters for the project.
Logs and commands
|
CONNECTIMU COM2 IMU_ADIS16488 |
|
LOG VERSIONB ONCE |
|
LOG HEADING2B ONNEW |
|
LOG RANGEB ONTIME 0.5 |
|
LOG TIMEB ONTIME 1 |
Data conversion
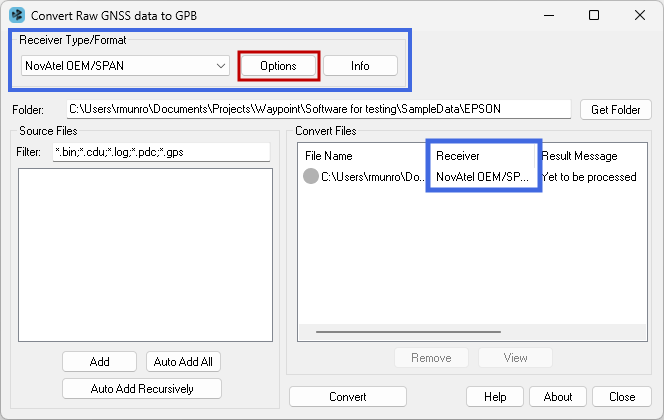
Data conversion can be done with the Convert Raw GNSS data to GPB Utility. Use the Get Folder button to browse to the folder containing the raw GNSS data, and then use the Auto Add All feature to add all raw GNSS data, including NovAtel data, for conversion. Auto Add All searches for any supported GNSS manufacturer data within the current folder. Auto Add Recursively searches the current folder and all sub-folders.
GNSS Raw Data Converter Utility – Auto-detect the NovAtel OEM7 / SPAN Receiver Type
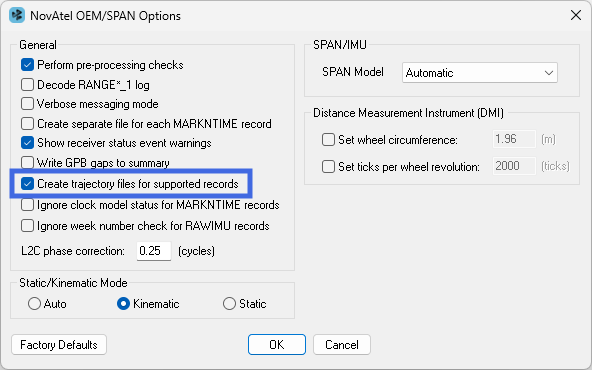
Several logs, specified in the Recommended logs list, are used to generate real time trajectory files during data conversion. After the raw data file is added, click the Options button and select the Create trajectory files for supported records option. After the data has been converted, the trajectory files can be loaded and viewed in Inertial Explorer to compare against the post-processed solutions.
GNSS Raw Data Converter Utility - Generate real time trajectory files during data conversion
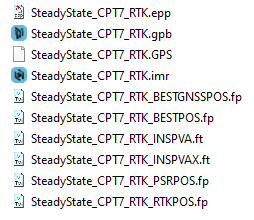
Data files
Depending on the type of data logged, several file types will be generated and saved in the same directory as the original raw data file. As shown in Figure: Files generated after raw data conversion of this example data set, the data used in this example generated the *.epp, *.gpb, *.hmr, *.imr, *.sta and real time trajectory files (*.fp and *.ft). Table: All possible file types generated from data conversion lists all the files which can be produced upon data conversion; not all data sets will contain the relevant data to produce all of these files. When the GPB file is loaded into the project as a Rover or Master, the other file types are also added.
Auto-fill set up parameters
With this data logged, converted, and added to the project, users can then auto-fill a variety of parameters in the Processing Settings. The following figures show the parameters filled using the logs recorded in the example data collection.
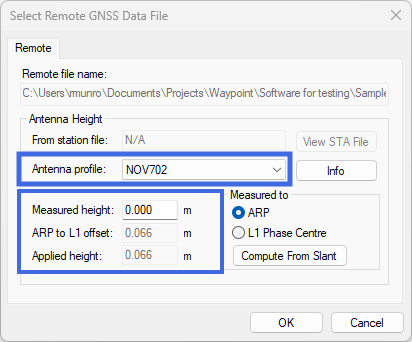
When adding a remote or base station file, the Antenna Profile will be auto-filled using information from the THISANTENNATYPEB log, read in from the STA file
The Lever Arm and IMU rotation will be auto-filled from the IMR file
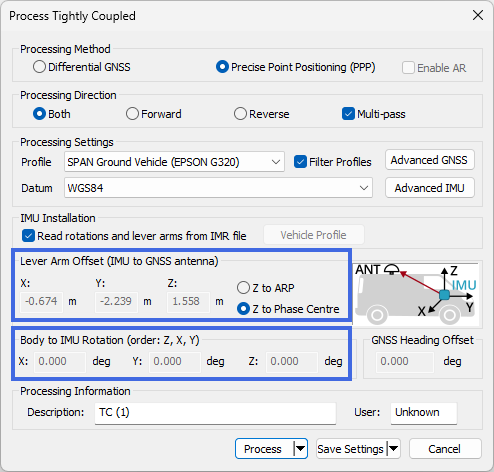
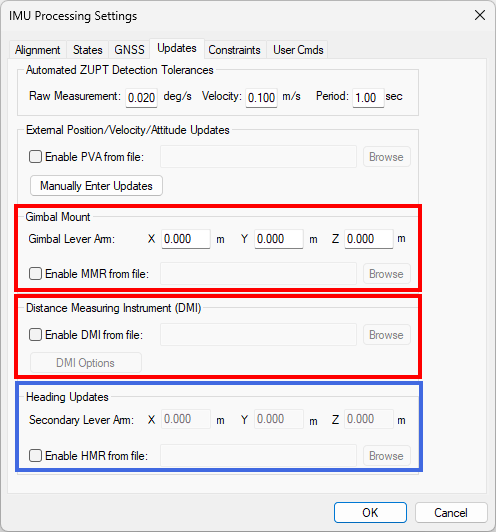
Dual antenna heading, odometer and/or mount data are auto-filled from the converted HMR, DMR and MMR files
Additional resources
OEM7 user manuals
Further details on the logs and commands outlined in this document can be found in the OEM7 Receiver Documentation Portal.
Waypoint Product Manuals:
Detailed instructions on using Inertial Explorer can be found in the Waypoint User Documentation Portal.
Support:
To search for more information or submit a support case, please visit NovAtel’s support page: www.novatel.com/support
APN-076: SPAN Data Logging for Inertial Explorer