In-line amplifier powered from an external power supply
Figure: In-line amplifier powered by an external supply illustrates an in-line amplifier that requires an external power source because the 200 mA provided by the receiver is not enough current. The in-line amplifier is powered directly via the bias-T and coaxial cable, with the DC power continuing on to the GNSS antenna LNA. The bias-T should include circuitry to prevent DC power from being fed back to the receiver and the ANTENNAPOWER OFF command must be issued to disable the GNSS receiver’s internal LNA power supply.
This configuration is also used if the in-line amplifier requires a input voltage other than +5 VDC.
Proper fusing or current limiting should be incorporated in the external power supply line.
In-line amplifier powered by an external supply
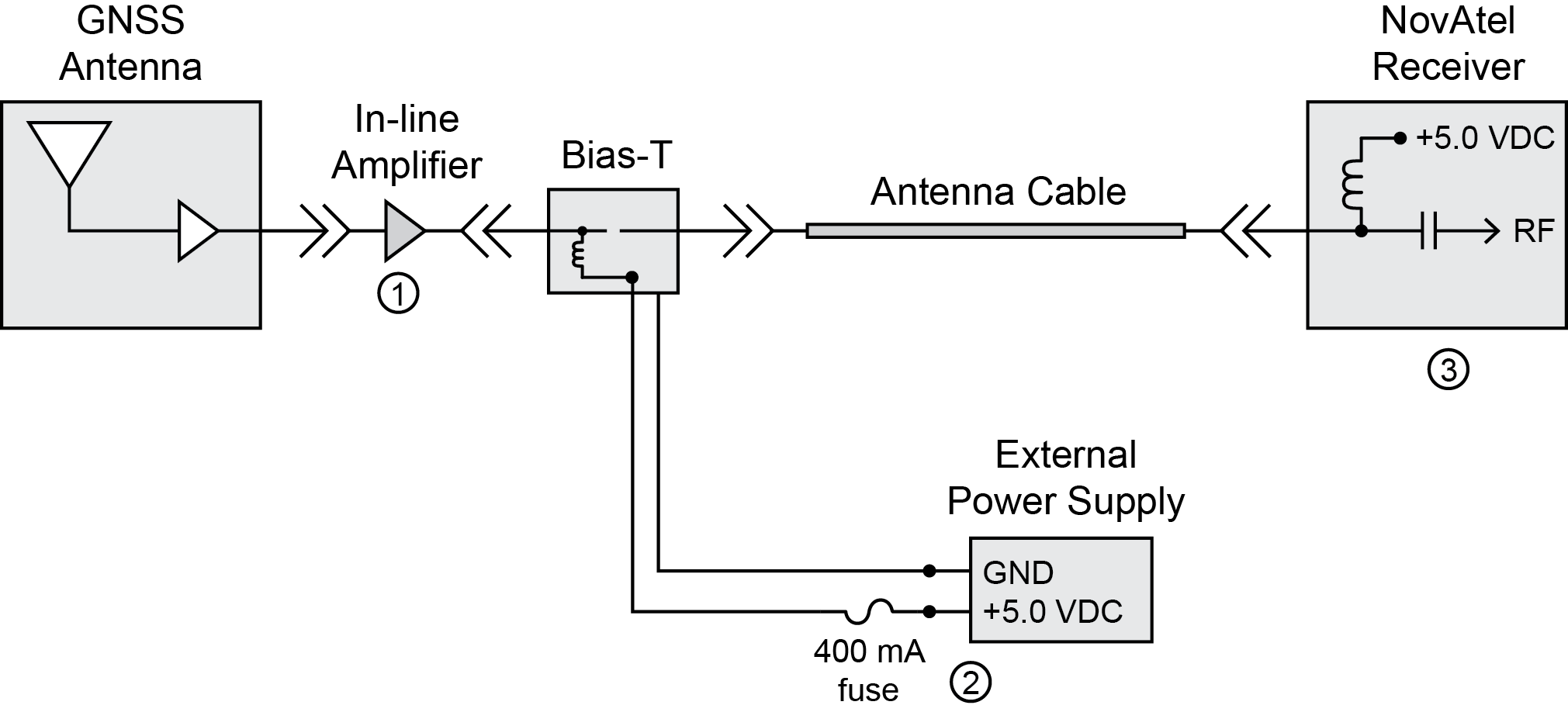
|
1 |
The in-line amplifier operates from power supplied via the coaxial cable centre conductor and is shunt-fed, which allows the DC power to continue down the coaxial cable to the antenna. |
|
2 |
The fusing and power supply requirements depend on the in-line amplifier and antenna. 400 mA and +5.0 VDC are examples shown for illustration purposes only. |
|
3 |
The ANTENNAPOWER OFF command must be issued to the receiver to disable the receiver’s internal LNA power output. |